ARC EM Software Development Platform¶
Introduction¶
The ARC EM Software Development Platform (emsdp) is an FPGA based development platform intended to support ARC licenses in developing their software for the ARC EM processor family and ARC EM Subsystems. It has the support for ARC EM4, EM5D, EM6, EM7D, EM9D and EM11D processors. ARC EM Enhanced Security Package (ESP) and ARC EM Subsystems (DFSS, SCSS, DSS) are also supported.
The EM Software Development Platform board includes the following features:
Support for selected ARC EM and ARC EM Subsystem configurations
Drag-and-drop configuration of FPGA device through USB
Audio PLL capable of generating the most common audio reference clocks
Analog audio input and output
MEMs digital microphone stereo input
16MB Quad-SPI flash memory supporting execute-in-place (XiP)
16MB Pseudo-Static RAM
Bluetooth 4.0, Wi-Fi a,b,g,n and 802.15.4 (e.g ZigBee) wireless connectivity
On board 9-axis motion sensors
Expansion connectors
1x Arduino UNO revision 3, over two connectors
3x PMOD connector (2x6 header)
1x MikroBUS
1x generic pin header
Micro-SD card interface for user data
Console output via a micro USB® connector
Multiple debug ports
Micro-USB (Digilent® Adept Xilinx® programming)
Cortex 10-pin Debug Interface (adapter to Ashling® Opella-XD for ARC debug)
Mictor 38 pin (Ashling Ultra-XD)
Buttons, LEDs and switches
The EM Software Development Platform contains the following components:
FPGA
Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7325T-2
Memory
PSRAM (16 MB)
SPI Flash (16 MB quad-mode XiP)
Configuration memory (16 MB SPI flash)
Interfaces
Audio line in/out
USB Data port (JTAG/UART/access to configuration memory)
Micro-SD Card
Wi-Fi/BT/Zigbee module
ADC (eight channels)
Motion Sensor
Digital MEMs microphone (2x)
RTT Nexus, JTAG
Extensions
Arduino Interface headers (UNO R3 compatible)
mikroBUS headers
Pmod Interfaces (3x)
Generic Pin Header (52 pins)
FPGA¶
The FPGA on the EM Software Development Platform board is configured by storing an FPGA bitstream into the configuration memory of the EM Software Development Platform. Drag-and-drop feature enable users to copy an FPGA bitstream from the PC to the configuration memory and programmed into the FPGA.
Memory¶
Please refer to ARC_EM_SDP_User Guide for memory map and more details.
Interfaces¶
EM Software Development Platform board provides a variety set of peripherals for evaluate and development. There are many peripheral devices available, such as SPI, IIC, UART, GPIO. Upon these, the EM Software Development Platform offers multiple interfaces for audio, USB, micro-SD card, wireless, ADC, motion sensor, etc. External hardware modules can also be easily connected to the board though extension interfaces using Pmod Connectors, Arduino, mikro BUS.
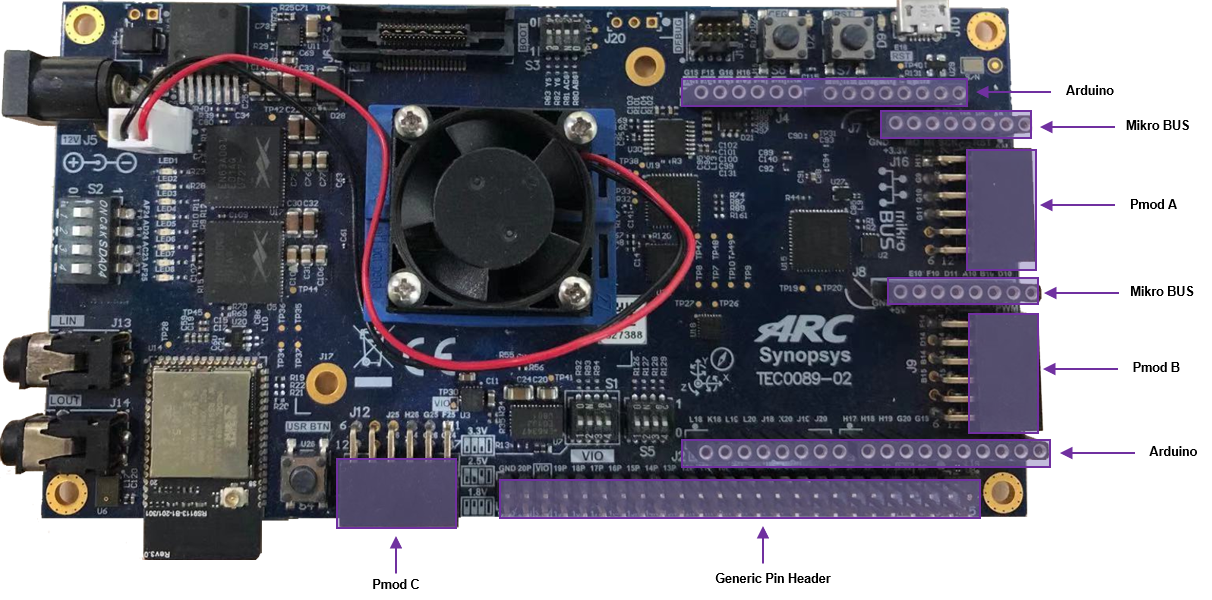
Extensions¶
To bring your application context around the EM Software Development Platform, Pmod Connectors, Arduino, mikro BUS are supported. All the sets of connections are controlled by mux controller and can be switched by user. There are many peripheral devices available, such as SPI, IIC, UART, GPIO.
Usage¶
Setting Up¶
You can use either USB-JTAG or USB-UART interface to communicate with EM Software Development Platform board. Before the interfaces are used, you must install the required drivers on the computer where you intend to run the MetaWare debugger or other serial debug consoles (such as PuTTY or other hyper-terminals).
The driver is a part of the Digilent Adept tool. You can download the most recent version of the Digilent Adept tool from the Digilent website, and follow the installation instructions provided by Digilent.
You may also skip this step if you are using default settings.
Note
Learn more about programming FPGA device in ARC_EM_SDP_UserGuide
Package Preparation¶
This section talks about how to add new EM Software Development Platform cores into embARC OSP. Please notice that the existing em11d_dfss core configure files are for test and example purpose, we strongly suggest you to follow the steps in this section.
You may download the package from our website: DesignWare ARC EM Software Development Platform. Suppose you want to add a new package called
em11d_dfss, then the name of your downloaded package would beemsdp_em11d_dfss.zip.Unzip the .zip file, you will find four folders:
/doc,/fpga,/include,/tool_config. Now create a new folder according to your board revision and package name. In this case em11d_dfss is added to rev2 board, so you should set your directory as this:/board/emsdp/rev2/configs/em11d_dfssCopy the contents of unzipped folder to
/board/emsdp/rev2/configs/em11d_dfss. It would be like:em11d_dfss ├─doc ├─fpga ├─include └─tool_config
You are done importing a new package, flash the bit file into your board and then build with it to make sure everything is working.
Build and Run Your First Program¶
By setting up the board, you are now ready to run your first program on EM Software Development Platform. There are two way to run your program. The first way is to use debugger, please refer to example example_blinky for further details. Build and download the example using either MetaWare or GNU. The command is shown below:
$ cd <embarc_root>/example/baremetal/blinky $ gmake BOARD=emsdp BD_VER=rev2 CORE=em11d_dfss TOOLCHAIN=mw run
Note
Notice that for CORE option there are multiple core choices, please check <embarc_root>/board/emsdp/rev2 folder for available cores.
The second way is to use a micro-SD card, the bootloader on EM Software Development Platform is capable to find and run prebuilt bin file that is named as app.bin.
Build the example using either MetaWare or GNU with the command shown below:
$ cd <embarc_root>/example/baremetal/blinky $ gmake BOARD=emsdp BD_VER=rev2 CORE=em11d_dfss TOOLCHAIN=mw bin
After building succeed, you will find blinky_mw_em11d_dfss.bin at <embarc_root>/example/baremetal/blinky/obj_emsdp_rev2/mw_em11d_dfss. Rename the bin file to app.bin and copy to the root directory of a micro-SD card. Insert the micro-SD card to EM Software Development Platform board and press start button to run.
Development Guide¶
Please refer to Developer Guides. You may need to specify peripheral driver (<embarc_root>/device/peripheral) for your own code.
For example, if Wi-Fi rs9113 driver is needed, add this line in makefile:
EXT_DEV_LIST += wifi/rs9113
Another example is to add both wifi driver and audio codec driver for an online audio application:
EXT_DEV_LIST += wifi/rs9113 audio/max9880a
Contributing¶
EM Software Development Platform is welcome to your contribution. If you found any bug or issue or have suggestions, please feel free to raise issues or pull requests at embARC Open Software Platform repository on GitHub.