Build System Documentation¶
Overview¶
The embARC build system is based on the makefile system as shown below. To add new components, add a new makefile to the system. All embARC components are compiled into libraries, which are then merged into one final library called libembarc.a. The application objects are then linked against libembarc.a to produce the target .elf file.
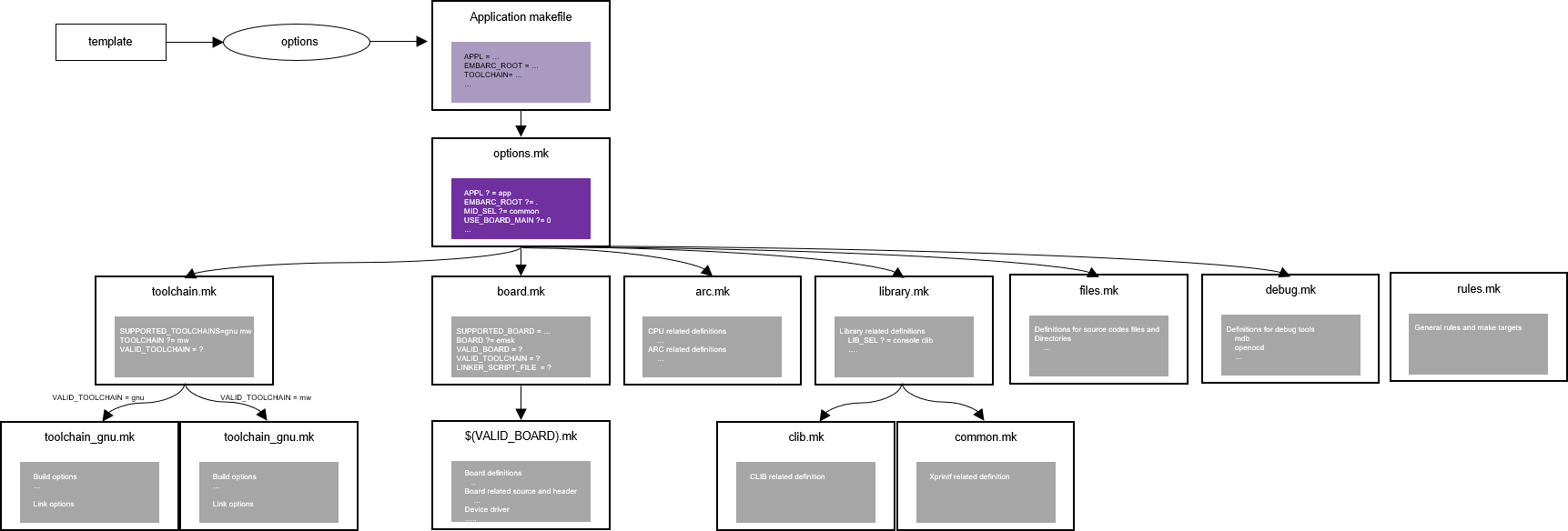
embARC build system¶
The options directory under the embARC root folder contains the common makefiles as shown below.
debug.mk: target debug options for the MetaWare debugger, which supports Ashling OpellaXD and Digilent USB-JTAG connections.files.mk: files and directory collections in embARC.options.mk: entry makefile with common definitions, path definitions, other makefiles, and so on.rule.mk: make targets and rules.scripts.mk: common makefile functionstoolchain.mk: general toolchain definitions, including toolchain_gnu.mk for the ARC GNU toolchain and toolchain_mw.mk for the MetaWare toolchain.toolchain_gnu.mk&toolchain_mw.mk: toolchain specific compile and link options
Make Targets¶
embARC build system is based on make. It can be used for both the MetaWare and ARC GNU toolchains, Windows and Linux development hosts, and multiple ARC cores and boards.
There are several targets to make and run embARC examples on the command line. These make targets are defined in options/rules.mk. All the commands below use the default make options provided in the embARC application makefile.
make help: Show help document about how to use make in embARC.
make all: Compile and link the target program.
make build: Clean current configuration object files and rebuild configuration.
make run: Compile and link the target program. For the MetaWare toolchain, call the MetaWare debugger (MDB) to load the target program to ARC board. For the ARC GNU toolchain, call arc-elf32-gdb and OpenOCD to load the target program to ARC board.
make gui: Compile and link the target program. Launch the MetaWare debugger (MDB) in GUI mode for the MetaWare toolchain or arc-elf32-gdb in command-line mode for the ARC GNU toolchain to debug the target program.
make clean: Clean object files for current build configuration.
make boardclean: Clean all object files for currently selected board.
make distclean: Clean all object files for different configurations.
make cfg: Print current configurations of embARC.
make opt: Print detailed configuration properties of embARC.
Note
If running <embARC>/example/baremetal/bootloader with make run in the command line, the default make options are enabled in the embARC application makefile. Run make cfg to see the configuration for this application.
Make Options¶
The make options are defined for embARC flexibility. They can be set through make command or hard-coded in the application makefile.
Options to Set Using Make Command¶
Most options are located in <embARC>/options/options.mk. If you change an option value in <embARC>/options/options.mk, it will affect all the applications. You can set the value of the options in your own application makefile for the specified hardware.
BOARD: Select the target board. The default value of this option is defined in board/board.mk. Optional values as below, default value is emsk. For example,
make BOARD=emskselects the EMSK board as the target board.
BOARD |
Description |
|---|---|
emsk |
EM Starter Kit |
axs |
AXS Board |
nsim |
Virtual Board based on nSIM |
hsdk |
ARC HS Development Kit |
BD_VER: Select the board version. The default value of this option is defined in one of the following makefiles according to the BOARD option. For example,
make BOARD=emsk BD_VER=22selects 2.2 as the EMSK target board version.For the EMSK board, three versions are supported in embARC: 1.1, 2.2, and 2.3. The optional values of BD_VER are 11, 22 and 23. The default value of BD_VER for the emsk board is 22.
For EMSK 2.0, 2.1 and 2.2, you can upgrade the firmware version to 2.3, and for EMSK 1.0, you can upgrade the firmware version to 1.1.
For the AXS board, one version is supported: 103. The optional value of BD_VER is 103. The default value of BD_VER for the AXS board is 103.
For the nSIM board, two versions are supported: 10, 1506. The optional value of BD_VER is 1506 and 10. The default value of BD_VER for the nSIM board is 1506.
For the HSDK board, one version is supported: 10. The optional value of BD_VER is 10. The default value of BD_VER for the HSDK board is 10.
BOARD |
Location of BD_VER Definition |
|---|---|
emsk |
board/emsk/emsk.mk |
axs |
board/axs/axs.mk |
nsim |
board/nsim/nsim.mk |
iotdk |
board/iotdk/iotdk.mk |
hsdk |
board/hsdk/hsdk.mk |
Note
The BD_VER must match the target BOARD version. For example, programs built for 1.1 cannot run on an EMSK 2.x board.
CUR_CORE: Select the core configuration for the specified board version. For example,
make BOARD=emsk BD_VER=23 CUR_CORE=arcem11dselects the arcem11d core configuration for emsk 2.3.For EMSK 1.1, the default value of this option is arcem6 defined in <embARC>/board/emsk/configs/11/core_config.mk.
Make option - CUR_CORE for EMSK 1.1¶ CUR_CORE
Description
arcem4
ARC EM4 core
arcem4cr16
ARC EM4CR16 core
arcem6
ARC EM6 core
arcem6gp
ARC EM6GP core
For EMSK 2.2, the default value of this option is defined in <embARC>/board/emsk/configs/22/core_config.mk. For EMSK 2.3, the default value of this option is defined in board/emsk/configs/23/core_config.mk. The default value for EMSK 2.2 and 2.3 is arcem7d.
Make option - CUR_CORE for EMSK 2.2 & 2.3¶ CUR_CORE
Description
arcem7d
ARC EM7D core
arcem9d
ARC EM9D core
arcem11d
ARC EM11D core
For AXS, the default value of this option is archs36 defined in <embARC>/board/axs/configs/103/core_config.mk.
Make option - CUR_CORE for AXS¶ CUR_CORE
Description
archs36
ARC HS36 core
For nSIM 1506, the default value of this option is arcemfull defined in <embARC>/board/nsim/configs/1506/core_config.mk.
Make option - CUR_CORE for nSIM 1506¶ CUR_CORE
Description
arcemfull
ARC EM core with full features
archs
ARC HS core
arcemsecureshield
ARC EM core with secure feature
For nSIM 10, the default value of this option is arcem defined in <embARC>/board/nsim/configs/10/core_config.mk.
Make option - CUR_CORE for nSIM 10¶ CUR_CORE
Description
arcem
ARC EM core
archs
ARC HS core
For HSDK, the default value of this option is archs38_c0 defined in <embARC>/board/hsdk/configs/10/core_config.mk.
Make option - CUR_CORE for HSDK¶ CUR_CORE
Description
archs38_c0
ARC HS38x4 core 0
archs38_c1
ARC HS38x4 core 1
archs38_c2
ARC HS38x4 core 2
archs38_c3
ARC HS38x4 core 3
TOOLCHAIN: Select the toolchain to compile the embARC software. For example,
make BOARD=emsk BD_VER=23 CUR_CORE=arcem11d TOOLCHAIN=gnuselects the ARC GNU toolchain to compile embARC applications for EMSK 2.3, ARC EM11d. The default value of this option is mw defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk
TOOLCHAIN |
Description |
|---|---|
mw |
MetaWare Development Toolkit |
gnu |
ARC GNU Development Toolset |
DIG_NAME: Specify the Digilent USB JTAG name. The default value of this option is empty defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk.
It is not necessary to set it when just one JTAG is connected to your PC. It is useful when more than one EMSK JTAG cable is connected to your PC, for example, to debug two EMSK boards using one PC. See Debug Multiple Boards for details.
This option is only available when the MetaWare toolchain is selected. This option is a simple wrapper of the -prop=dig_device=name option for the MetaWare debugger (mdb). See MetaWare Debugger User’s Guide for details.
V: Control whether to show verbose compiling information. The default value of this option is 0 defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk.
V |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Show basic compiling information |
1 |
Show verbose information |
TCF: Select the tool configuration file (tcf). You can choose the specified tcf file by this option for the target board and core configuration.
This option uses absolute file path or relative file path (relative to where your application makefile located) to specify the tcf file .
This option is not supported for the nSIM 1506 board.
For example, when the current board and core is EMSK 2.3 and ARC EM7D, you can pass your own tcf file arcem.tcf to replace the default one. Copy arcem.tcf file into the folder where application makefile located. Run
gmake BD_VER=23 CUR_CORE=arcem7d TCF=arcem.tcfto select it.
Note
When selecting you own tcf file, clean the project before build it.
Options Coded in Application Makefile¶
ARC related Options
OLEVEL: Select the compiler optimization level, including O, O0, O1, O2, O3, Os, Os1, Oz, Ofast, Og. The default value of this option is defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk. The OLEVEL can be blank to not select any optimization, like OLEVEL=.
For example,
make BOARD=emsk BD_VER=22 CUR_CORE=arcem11d TOOLCHAIN=gnu OLEVEL=O2selects optimization level O2 of the ARC GNU toolchain to compile embARC applications for EMSK 2.2 and ARC EM11D.
JTAG: Select the JTAG probe to load and debug the target program. The default value of this option is usb defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk.
For example,
make BOARD=emsk BD_VER=22 CUR_CORE=arcem11d OLEVEL=O2 TOOLCHAIN=gnu runselects the ARC GNU toolchain to compile embARC applications with optimization level O2 for EMSK 2.2, ARC EM11D, and load the applications using Digilent USB JTAG.
JTAG |
Description |
|---|---|
usb |
Digilent USB JTAG cable |
opella |
Ashling Opella-XD JTAG probe |
Note
opella is only supported for the MetaWare Development Toolkit.
OS_SEL: Select operating system. This option should be defined in your application makefile. Set this option in the makefiles if OS services are required.
JTAG |
Description |
|---|---|
freertos |
FreeRTOS Runtime |
Note
Leave the OS_SEL value blank OS_SEL= to use bare-metal runtime.
MID_SEL: Select middleware to be used in embARC application. This option should be defined in your application makefile.
All available middleware packages are located in <embARC>/middleware. You can access them by their folder name, such as ntshell or fatfs.
√ means this middleware is supported in this environment, and x means not supported.
Middleware dependencies
aws middleware required mbedtls middleware.
coap, mqtt, and lwm2m are only for FreeRTOS. and require lwip and lwip-contrib.
mbedtls require fatfs middleware to provide file access in some cases.
lwip middleware is only for FreeRTOS.
openthread middleware requires mbedtls to support encryption.
Middleware |
MID_SEL |
Baremetal |
FreeRTOS |
|---|---|---|---|
AWS IoT Device SDK |
aws |
x |
√ |
CoAP |
coap |
x |
√ |
Common |
common |
√ |
√ |
FatFs |
fatfs |
√ |
√ |
HTTP Parser |
http_parser |
√ |
√ |
iHex |
ihex |
√ |
√ |
JSON |
parson |
√ |
√ |
lwIP |
lwip lwip-contrib |
x |
√ |
LwM2M |
wakaama |
x |
√ |
mbed TLS |
mbedtls |
√ |
√ |
MQTT |
mqtt |
x |
√ |
Nt-Shell |
ntshell |
√ |
√ |
OpenThread |
openthread |
√ |
√ |
U8glib |
u8glib |
√ |
√ |
Note
It is recommended to include common middleware to provide basic printf() functionality using xprintf().
LIB_SEL: Select libraries to be used in the embARC application. This option should be defined in your application makefile. All available libraries are located in <embARC>/library. clib* is set as default.
LIB_SEL |
Description |
|---|---|
clib |
C Library Support |
secureshield |
SecureShield Library |
APPL_LIBS: Set extra required application libraries to be linked. This option should be defined in your application makefile.
This APP_LIBS option collects extra linker option to include extra libraries to be linked.
For example, APPL_LIBS = -lm means linking math library to target program. -lm only support the ARC GNU toolchain.
HEAPSZ: Set application heap size in bytes. This option should be defined in your application makefile. The default value of this option is 8192 defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk. It means the heap size of the application is set to 8192 bytes by default.
HEAPSZ is useful for baremetal applications. For FreeRTOS applications, you can define the RTOS heap size by setting configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE in FreeRTOSConfig.h.
STACKSZ: Set application stack size in bytes. This option should be defined in your application makefile. The default value of this option is 8192 defined in <embARC>/options/options.mk. It means the stack size of the application is set to 8192 bytes as default.
For baremetal and Contiki applications, STACKSZ is useful for baremetal applications. For FreeRTOS applications, you can define the minimum RTOS task stack size by setting configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE in FreeRTOSConfig.h, and define each task’s stack size in the application source code.
USE_BOARD_MAIN: Control which board init process is used. The default value of this option is 1 defined in <embARC>/board/board.mk.
When USE_BOARD_MAIN is 0, it uses the normal board init process, compatible with previous embARC releases; you must do board_init yourself.
When USE_BOARD_MAIN is 1, embARC initializes fatfs, ntshell, and lwip with WiFi and creates a FreeRTOS task for main(). You can write applications or create new tasks in the main() function. When ntshell is enabled, the main() function needs to be triggered by the ntshell main command.
Note
For more details about how this new process is implemented, see <embARC>/board/board.c. In most embARC examples, you don’t need to change USE_BOARD_MAIN to 0.
EXT_DEV_LIST: Select peripheral device drivers used in your application.
Use EXT_DEV_LIST in the example’s makefile. If more than one peripheral device drivers are selected, please use space between each other, like EXT_DEV_LIST += EXT_DEV_LIST += wifi/mrf24g sensor/temperature/adt7420.
Optional values for EXT_DEV_LIST can be found in <embARC>/device/peripheral. Select the target peripheral device drivers relative path, and add it to EXT_DEV_LIST.
Some onboard peripheral device drivers are already selected according to the target board, you can check it in the target board makefile, such as <embARC>/board/emsk/emsk.mk.
Note
WIFI_SEL is not available now. If choosing different WiFi, you need to change the EXT_DEV_LIST in your example makefile.
EMBARC_ROOT: Set embARC source-code root directory path. This option should be defined in your application makefile to specify the path of the embARC source-code root. The path can be relative or absolute.
Application related Options
APPL: Set embARC application name. APPL should be defined in your application makefile.
APPL_CSRC_DIR: Set the path of application C source-code directories. APPL_CSRC_DIR should be defined in your application makefile.
All C source-code directory paths including subfolders should be added.
C source-code files should be suffixed with c or C, such as .c or .C.
The paths are separated by whitespace.
APPL_ASMSRC_DIR: Set the path of application assembly source-code directories. APPL_ASMSRC_DIR should be defined in your application makefile.
All Assembly source-code directory paths including subfolders should be added.
Assembly source-code files should be suffixed with s or S, such as .s or .S.
The paths are separated by whitespace.
APPL_INC_DIR: Set the path of application include-file directories. APPL_INC_DIR should be defined in your application makefile.
All include-file directory paths including subfolders need to be added.
The paths are separated by whitespace.
APPL_DEFINES: Set extra macros defined from makefile for this application. APPL_DEFINES should be defined in your application makefile.
All macro definitions are separated by whitespace.
For example, if you want to define USE_EMBARC=1, then you should set the value to -DUSE_EMBARC=1.
Additional compiler, assembler, and linker options
ADT_COPT: Additional compiler options. See the compiler manual for help.
ADT_AOPT: Additional assembler options. See the assembler manual for help.
ADT_LOPT: Additional linker options. See the linker manual for help.